UMMC provides patient-centered treatment, clinical excellence, and an advanced level of care unavailable anywhere else in the state.

for Kids.
Children’s of Mississippi is here for every child
with the state’s only children’s hospital
plus clinics statewide.
Latest News
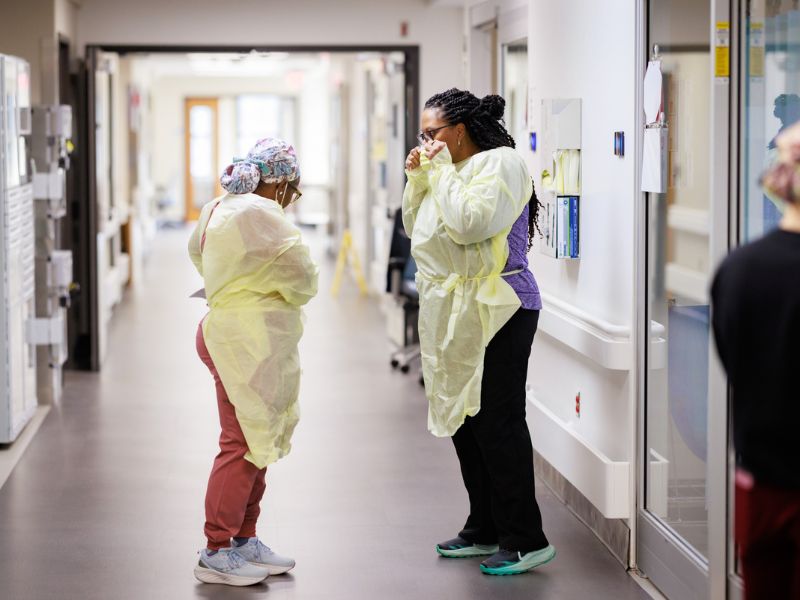

UMMC opens dedicated burn unit to expand statewide care
Monday, May 5, 2025
UMMC opened a new dedicated burn unit, expanding its ability to care for both pediatric and adult patients with serious burn injuries. The specialized unit is designed to deliver advanced, coordinated treatment from emergency care through rehabilitation, all in one centralized location. Read More
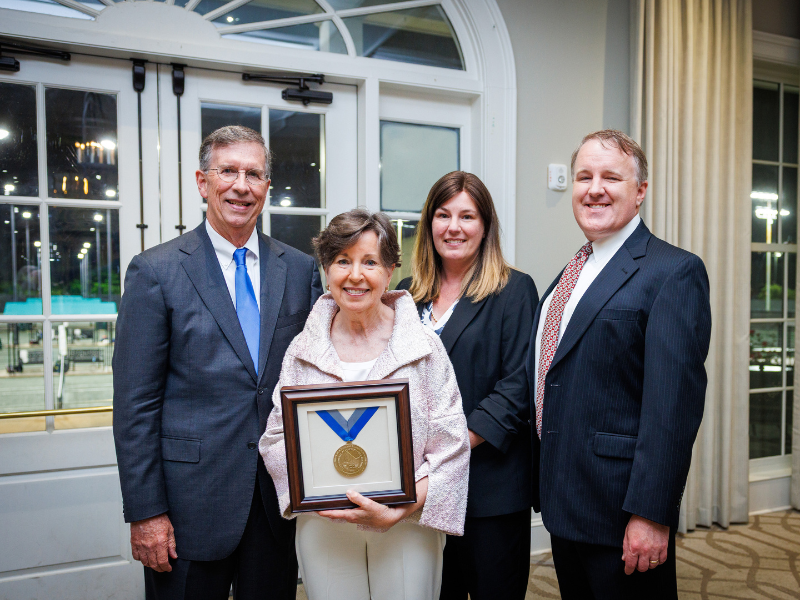

Endowed chair in obstetrics and gynecology honors Dr. James N. Martin Jr. and Dr. Gloria Howard Martin
Monday, May 5, 2025
Dr. James Nello Martin devoted his life to advancing maternal-fetal medicine and improving outcomes for women and babies. Now, a $1 million endowed chair established in his and his wife Dr. Gloria Howard Martin’s name will carry that legacy forward at the University of Mississippi Medical Center. Read More
Latest Articles
#2025UMMCGrad: Experience leads to innovation for Liza Owens
Published on Monday, May 5, 2025

Faculty members, clinics are national-level exemplars
Published on Monday, May 5, 2025
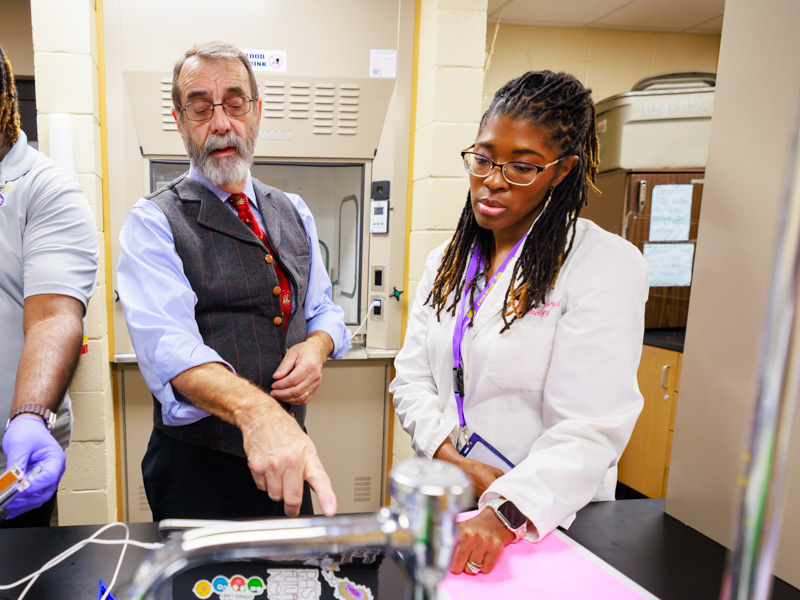

Base Pair expansion powers the promise of future researchers
Published on Monday, May 5, 2025
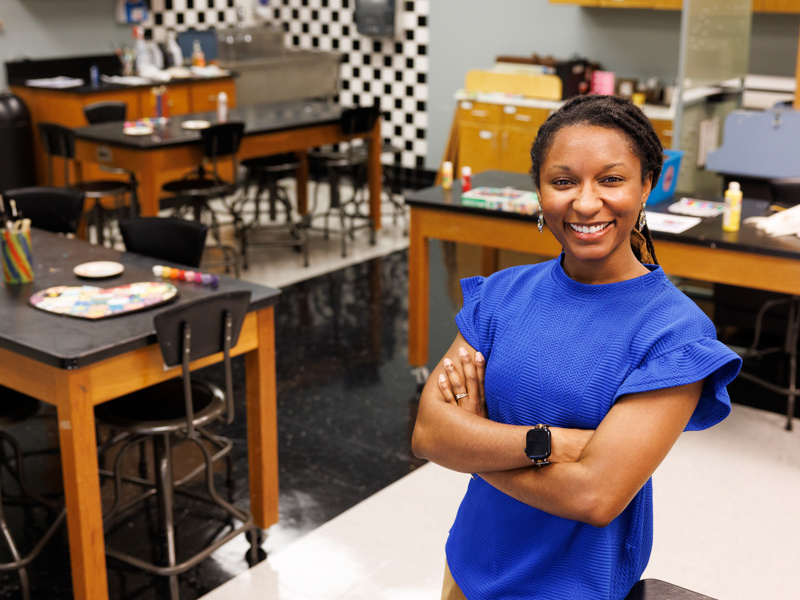

Front and Center: Iesha Smith
Published on Monday, April 28, 2025
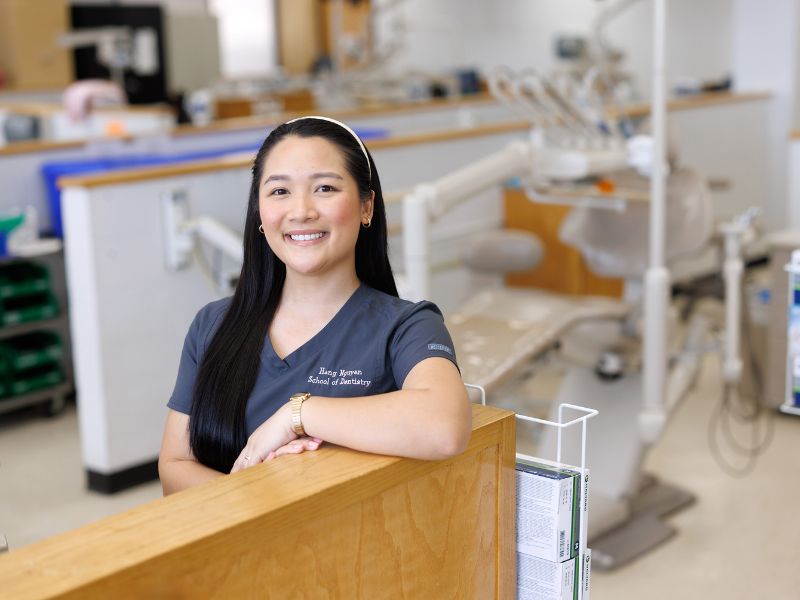

#2025UMMCGrad: Hang Nguyen
Published on Monday, April 28, 2025
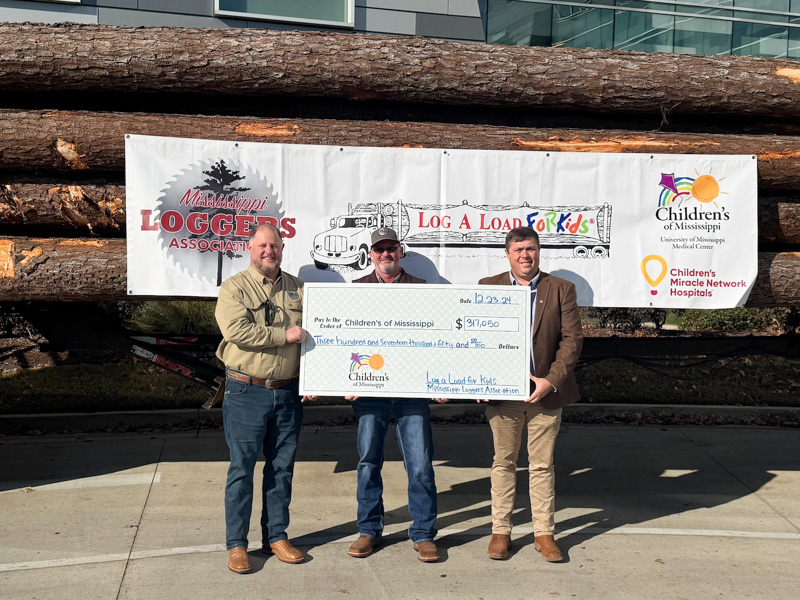

Mississippi Loggers Association has towering record of support for Children’s of Mississippi
Published on Monday, April 28, 2025
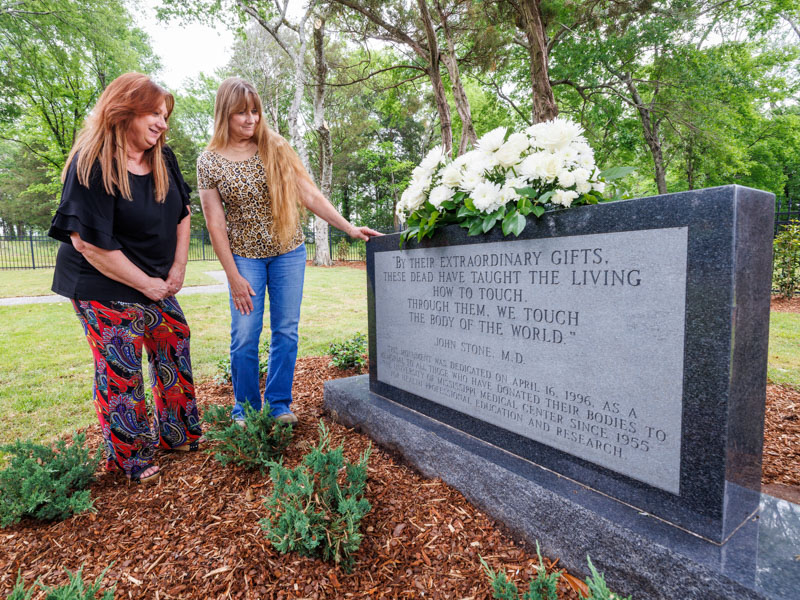

Ceremony celebrates those who gave a gift like no other
Published on Monday, April 28, 2025

Scientists, epilepsy centers, children’s advocate commended
Published on Monday, April 21, 2025
Find Us on Social Media
Get news and information you need about the Medical Center by connecting with us through our social media community. You’ll find events, news stories and campus activities shared daily. UMMC is active on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, YouTube and LinkedIn.
You may also connect with the Children’s of Mississippi social media community on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram and YouTube.
Follow Dr. LouAnn Woodward on Twitter.
We look forward to hearing from you!
Sign Up for Consult

Connect with UMMC via new e-magazine
In CONSULT, readers will have the opportunity to learn more about the cutting-edge clinical advances, innovative educational programs and groundbreaking research occurring at UMMC. Plus, CONSULT will regularly showcase our experts' best advice for living a healthy and mindful life.






